The Threshold HSV/HSL function is available on the Image menu.
When you select this option it shows the following window.

This option is similar to the Threshold RGB process, except that instead of selecting pixels on the Red, green and Blue components of their colour, it selects pixels by either their hue, saturation and luminance (HSL), or hue, saturation and value (HSV).
Hue is the same in both the HSL and HSV colour models, but saturation is defined differently in each, and luminance is not the same as value.
Here is how to visualise the HSV colour model:
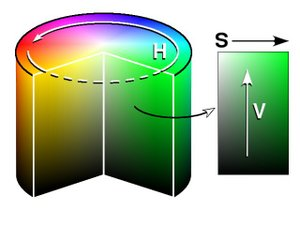
|
Because hue is represented as a circle, it is measured in angular degrees from 0 through to 360.
Zero degrees is pure red, 60 degrees is yellow, 120 degrees is green, 180 degrees is cyan, 240 degrees is blue, 300 degrees is magenta and 360 degrees is back to red.
Saturation and value both range from 0 through to 100%. At full saturation and full value (100%) the hue is most intense. As the saturation is decreases the colour moves towards white. But as the value decreases the colour moves towards black. |
And here is how to visualise the HSL colour model...

|
Again, hue is represented as a circle, and it is measured in angular degrees from 0 through to 360.
Zero degrees is pure red, 60 degrees is yellow, 120 degrees is green, 180 degrees is cyan, 240 degrees is blue, 300 degrees is magenta and 360 degrees is back to red.
Saturation ranges from 0 throught o 100%. At full (100%) saturation the hue is most intense, and at least saturation the colour is grey. Luminance ranges from 0 through to 100%. At zero luminance the colour is black. At 100% luminance the colour is white. In the HSL model the colour is most intense at 50% luminance, according to the saturation. |
You can use whichever colour model you are more familiar with (or the one that gives the result you want).
Thresholding in HSV or HSL can be very useful for isolating or removing image features which cannot be achieved by the RGB thresholding when the pixel colour range is diverse.
In the example window above, the RGB colour is completely ignored in the thresholding operation because the hue range is 0 through to 360 degrees. The image stippled background is completely removed just by the saturation and luminance ranges.
If you need to specify a hue range that spans the 0 or 360 degrees point (red) then you can give the Low hue as higher than the High hue. For example, if Low=300 and High=60 then the hue range is from magenta through to yellow.
Related Topics: